Why A Lean StartUp Equals Success More Often
The term ‘risky business’ wasn’t coined for any old reason.
Whether you’re a large company, a small company, or a soon-to-be company there is always of chance of landing on major failure instead of major success in the business coin flip. Infact, 70% of startups fail with only 10% of startups actually making any money. So how do you guarantee success for your startup? The Lean Startup is a trick coin of sorts, and can engineer startup success if you follow the process.
The lean startup
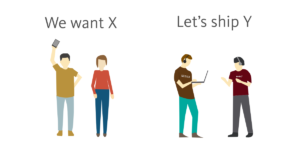
The lean startup is a business methodology that encourages ventures to be more innovative, successful and is an avenue to stop wasting people’s time and money. Differing from traditional business methods, where a plan is created in advance on the basis of some ‘good guesses’ by outlining a static solution to an identified problem in spite of all the unknowns. These business plans are often written in full and set in stone before any market research, funding, product development or testing has even begun. Typically, they cover the future implementation of a 5 year plan which assumes acquisition, earnings and money going in and out of the business even though the concept may be no where near it’s execution- perhaps months or even years into the future.
Once all the pre-planning is done and investors somehow find value in these estimated numbers, it’s taken into development. Time and money, among other resources, are freely thrown around with the product finally coming in contact with consumers only after its completion and launch. This is an example of when a venture has spent its time and money in a wasteful manner; the product hits the market with no customer adoption and the sales flop. Why? Because too many entrepreneurs think they can forecast unknowns. It’s a fantasy to think you can execute a dreamt up business model and still create a product that customers really want; all while having done nothing in terms of conducting product testing or market research to validate the idea. They then fail to get a place in the market because they never bothered to see if anyone even thought the app was useful, a prime example of when startups get carried away and start creating an app for themselves instead of for the consumer.
The lean startup acknowledges that the existence of all these ‘good guesses’ at the beginning of any business plan are simply hypotheses that require testing, and aims to teach you how you can develop your business product through a much less wasteful practice while providing a solution to the risks of the unknown. This is why they start off by filtering all of these assumptions into the business model canvas framework to devise how the product can create value for its customers, as well as set them apart from any other solution that already exists. The lean startup also suggests that you should put the idea of getting rich quick out of your mind for the time being, and really focus on analyzing and meeting the specific needs/demands of your market in the most efficient, affordable way possible.
Ways the Lean Startup tests these hypotheses.
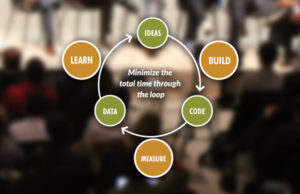
The Build – Measure – Learn Feedback Loop
Sounding pretty self explanatory, the build – measure – learn feedback loop is a learning cycle of building on the business plan, measuring it’s effectiveness and learning from the findings of conducted research. It allows the developers to either persever with the idea-turned-product, making slight tweaks and adjustments here and there, or to pivot away from the idea toward something more sustainable.
Pivoting occurs when you’ve further advanced your business model or built your product, conducted testing to get feedback and issues have arised that cannot be solved by just tweaking and re-building the product. Pivoting is a structured correction or change of path that allows you to test new strategies or product features. Its repetition is fundamental to further advancing the business model and is employed to help you identify and get closer to the product market fit.
Product Market Fit.
Product market fit is the point of development where you have found the product that your customers really want and would be at a loss without. Research findings help to further develop or pivot your product in order to identify the appropriate product market fit.
Customer Development
Customer development is a form of market research used to test hypothesis, get an insight on potential users and provide feedback on elements such as pricing, distribution channels and it’s core features. It focuses on failing quickly and improving quickly,ensuring that time is not wasted on unnecessary features or creating an app that the consumer doesn’t actually want or need. Feedback can be drawn from several experiments and tests, those being:
MVP
Many startups like to keep their golden idea hush hush, in fear of exposing prototypes and having the dream yanked out of their hands before anything tangible comes about. In traditional methods, the beta version of an app would be the first time any consumer came into contact with the concept. The lean startup actually discourages secrecy. This is because customer feedback is held highly in terms of value, as constant feedback allows for more tailored development will increase success in terms of getting a desired product in the hands of the target market as soon as possible.
A key element of the methodology is the release of an MVP (minimum viable product) to help you shorten your product development cycle and minimise the outside funding required to create the perfect product for your target customer. An MVP is a first release, stripped down version of your app and can give you valuable customer feedback that your company can then use for further development to make your app more attractive to the target consumer. It is used to revise and correct the assumptions that have been made, then start the cycle over again, constantly testing every tweak and making iterations constantly to ideas that aren’t working. You can read more about why an MVP is important, here.
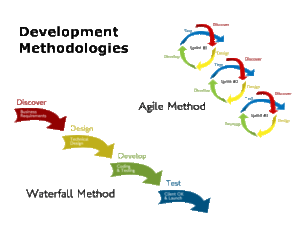
Agile Development
Aiming to eliminate wasted time, agile development proposes alternatives to a waterfall method and exists to remove the yearlong product development cycle by developing the product iteratively and incrementally, this is how the the final version of an MVP is created for release in a more timely fashion.
Continuous Deployment
Continuous deployment refers to the software development side of the product only, and is a way to significantly decrease cycle times. It entails the immediate deployment of all new code that has been written, meaning that instead of storing all the new changes for weekly updates there could be up to hundred of updates everyday for quick testing, feedback and re-development. It is an umbrella term and involves practices such as iterative product releases and continuous integration, which stops errors from being integrated by producing code several times a day for improvements and re-realsing after every development cycle or iteration.
Validated Learning
When validated learning is embraced, the development process time can be significantly reduced. It involves testing initial ideas to get insight on how potential customers would interact and respond, either validating the effect or proving it useless. It allows you to bypass the traditional business method of spending months developing a product then only having its issues identified once it’s in beta. It explores how the product can be tweaked to ensure you’re building the right product for your customers by adapting your app plans incrementally. Conducted repeatedly, it can be a faster, more efficient way of fixing problems. Helping your startup to learn about and apply changes for further testing so that errors are only made once.
Split Testing
Split testing can help you make decisions if you’re juggling between different versions of features or methods of navigation. It is an experiment that gets a controlled group of customers, splits them into 2 or more groups and gives them each a different version of the app for testing. It provides clarification as it allows controlled observation on how each group interacts and behaves with each version, the comparison can provide an understanding of which features are more useful, effective or unnecessary.
Success must first begin with failure, and if you think you’re going to get it right the first time you’re absolutely dreaming. Before when we spoke about 70% of startups failing, that failure is due to a lack of customers rather than a collapse due to product development. The lean startup emphasises the ability to blossom from failure, revising initial ideas and adapting to everything they learn about the target customer throughout the process. Putting emphasis on customer experience and feedback than planning based on assumptions and intuition.